Harbour
Time:
The time interval between the peak of the moon and the high tide
is almoust constant. This interval is called the Harbour Time of
a place. For the peninsula Spurnpoint this comports about 5 hours.
Die Eintrittszeit der Flut folgt an jedem Küstenort nach Ablauf einer gewissen Zeitdauer dem Durchgang des Mondes durch den Ortsmeridian. Diese Zeitdauer schwankt nur wenig um einen Mittelwert, den man die Hafenzeit des Ortes nennt. Auf der Halbinsel Spurnpoint beträgt diese circa 5 Stunden.
tides,
low tide, high tide:
sea-level oscillation of approximately daily or twice daily period; the
movement is caused by the difference of the gravitational attraction between
celestial bodies and the centrifugal acceleration of their rotation, and
is periodic because it is related to the motion of the sun, earth and
moon. The minimum sea-level is called low tide, maximum sea-level is called
high tide.
Gezeiten:
das abwechselnde Steigen (Flut) und Fallen (Ebbe) der Oberfläche des
Meeres und damit verbundener Binnengewässer, soweit diese Bewegung
durch die Gravitation des Mondes und der Sonne entsteht.
spring tide:
tide of maximal range, near the time of New and Full Moon when the sun
and moon are in syzygy - i.e. aligned with the earth. Conjunction is a
time during New Moon when the sun and moon lie on the same side of the
earth; opposition is the other syzygy condition that occures during Full
Moon when the sun and moon are positioned on opposite sites of the earth.
In either case of syzygy, the tide-producing forces of the sun and the
moon reinforce each other, and the tidal amplitudes on earth are at their
greates.
besonders großer Hub nach Voll- oder Neumond
neap tide:
tide of minimal range occuring near the time that the moon and sun are
in quadrature. This condition is geometrically defined as the time that
the line from the earth to the moon is at right angles to the line from
the earth to the sun. Thus, the tide-producing effects of the sun and
the moon cancel each other, and tidal ranges are usually 10 to 30 percent
less than the mean tidal range. Quadratura and neap tides occur twice
each synodic month.
besonders kleiner Hub nach dem ersten und letzten Mondviertel
time:
As specification of the entire time units acts the periodically rotation
of the earth around its axis during its simultaneous circulation around
the sun.
The solar day is measured by the time between two successing culminations of the sun. The solar day is not an exakt time unit: Its length is not constant because of the irregular movement of the earth in its elliptical orbit around the sun.
Bis heute dient zur Festlegung sämtlicher Zeiteinheiten die sich periodisch wiederholende Rotation der Erde um ihre Achse während des gleichzeitig stattfindenden Umlaufs um die Sonne.
Der wahre Sonnentag wird gemessen als die Zeit zwischen zwei aufeinanderfolgenden Kulminationen der Sonne. Der wahre Sonnentag ist indessen keine exakte Zeiteinheit, denn seine Länge schwankt, bedingt durch die ungleichförmige Bewegung der Erde in ihrer Bahnellipse um die Sonne. Man wählt daher als bürgerliche Zeiteinheit den mittleren Sonnenstand, das ist die Zeit zwischen zwei Kulminationen eines fingierten Gestirns ("mittlere Sonne"), welches man sich am Himmelsgewölbe derart gleichförmig bewegt denkt, dass es in seiner Stellung immer nur wenig von der wahren Sonne abweicht und zu gewissen Zeitpunkten des Jahres (4mal) die gleiche Stellung wie diese innehat.
solar
time:
the local time by the solar SUNPOSITION. Noon is always when the sun goes
through the meridian, what means it stands at its peak. The solar time
differs from the mean solar time by the equation
of time.
die Uhrzeit an einem Ort nach dem wahren Sonnenstand. Mittag ist immer dann, wenn die Sonnen durch den Ortsmeridian geht, dass heisst am höchsten steht. Sie differiert von der mittleren Ortszeit um die Werte der Zeitgleichung.
mean
solar time:
the time corrected by the equation of time,
that is related to the imaginary regular movement of the sun.
die um die Werte der Zeitgleichung korrigierte Zeitangabe, die sich auf einen gedachte gleichförmige Bewegung der Sonne bezieht.
equation
ot time:
the difference between solar time and mean solar time is due to small
asymmetries in the orbit of the earth around the sun.

Zeitgleichung:
Unterschied zwischen der wahren Ortszeit (WOZ), resultierend
aus dem wirklichen, jahreszeitlich unregelmäßigen Gang der
Sonne entlang der Ekliptik und zwischen der mittleren Ortszeit (MOZ),
resultierend aus einem angenommenen gleichmäßigen Gang der
Sonne.
MOZ-WOZ = "Zeitgleichung"
time zone:
time normally shown by clocks, as system of timekeeping in which the same
time is kept throughout each of 24 zones and the time in any zone differs
by an integral number of hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
The zones on the average are spaced 15° of longitude apart, though
their boundaries commonly coincide with those of political subdivisions
to avoid inconvenient changes in time. The standard time in each zone
was the mean solar time of its central meridian. Since 1972, however,
mean solar time has been replaced by UTC. A few areas keep times that
do not differ by a whole number of hours from UTC.
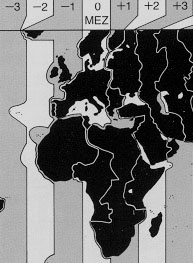
Zone von duchschnittlich 15° Länge, für die dieselbe gesetzliche Zeit gilt. Der Zeitunterschied von Zone zu Zone beträgt jeweils eine Stunde.
daylight saving:
Means of fitting the ordinary daytime schedule of activities into the
daylight hours by setting the clock one hour ahead of local standard time
during the summer.
Die im Sommer (meist um eine Stunde) gegen die Einheitszeit vorverlegte Uhrzeit.
CET (central european time):
The local meantime of the 15. longitude east.
Sie entspricht der mittleren Ortszeit des 15. Längengrad Ost.
WET
(western european time):
The local meantime of the prime meridian (CET minus one hour). It is the
official time in Great Britain and is also called universal time (UTC).
Sie entspricht der mittleren Ortszeit des Nullmeridians. MEZ minus eine Stunde. Offizielle Zeit in Großbritannien. Sie wird auch Weltzeit genannt.
latitude:
coordinate system by means of which the position or location of any place
on the earth's surface can be determined and described. Latitude is a
measurement on a globe or map of location north or south of the equator
given in degrees, minutes, and seconds, geographical latitude is the arc
subtended by an angle at the centre of the earth and measured in the north-south
plane poleward from the equator.
Verbindungslinie von Orten mit gleichem Abstand zum Äquator, daher auf ihn bezogen, auch Parallelkreis genannt, auch Winkelabstand eines Punktes der Erdoberfläche von der Äquatorebene aus gemessen; die übliche Bezeichnung ist phi.
longitude:
longitude is a measurement of location east or west of the Prime Meridian
of Greenwhich, the specially designated imaginary north-south line that
passes through both geographic poles and Greenwhich, London.
Winkelabstand eines Punktes der Erdoberfläche, bezogen auf die Nullmeridianebene, gemessen in östlicher und westlicher Richtung. Der Nullmeridian wurde durch die Sternwarte von Greenwich (London) gelegt.
zenith:
point on the celestial sphere directly above an observer on the earth.
Zenit:
der Scheitelpunkt des Himmelsgewölbes, liegt lotrecht über dem
Beobachter, dem Nadir entgegengesetzt.
nadir:
the point 180° opposite the zenith, directly under foot, is the nadir.
Nadir:
Fußpunkt, Gegenpunkt des Zenit an der Himmelskugel.
azimuth
and altitude:
any direction in space
may be defined by two coordinates, the azimuth and the altitude. The altitude
is the angular distance above the horizon.
the altitude is
At the horizon 0º
At the zenith 90º
At the nadir -90º
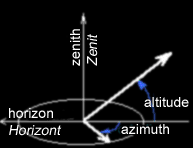
Azimutwinkel
/ Altitude:
Jede Richtung im Raum wird von zwei Koordinaten definiert, dem Azimuthwinkel
und der Altitude. Die Altitude gibt den Winkel vom Horizont gemessen an.
die
Altitude beträgt:
Am
Horizont 0°
Am Zenit 90°
Am Nadir -90°
(summer/winter) solstice:
In astronomy, either of the two points at which the sun reaches its greates
declination north or south. Each solstice is upon the ecliptic. Midway
between the equinoxes and, therefore, 90° from each. The term is also
applied to the time at which the sun reaches the point thus defined (about
june 21 and december 23).
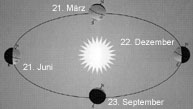
(Sommer-/Winter-) Sonnenwende, Solstitium:
Zeitpunkt des Höchsten oder Tiefsten Standes der Sonne bei ihrem
scheinbaren jährlichen Lauf an der Himmelskugel (+/-23.5°). Am
21./22. Juni steht die Sonne auf der Ekliptik im nördlichen Wendepunkt:
Die Nordhalbkugel der Erde hat ihren längsten Tag und Sommeranfang.
Am 21./22. Dezember, wenn die Sonne im südl. Solstitial steht, gilt
das Entsprechende für die Südhalbkugel; die Nordhalbkugel hat
dann den kürzesten Tag und Winteranfang.
equinox:
either of the two moments in the year when the sun is exactly above the
equator, and day and night are of equal lenght; also, either of the two
points in the sky where the ecliptic and the celestial equator intersect.
The vernal equinox, marking the beginning of spring in the northern hemisphere,
occures about march 21, when the sun moves north across the celestial
equator. The autumnal equinox falls about september 23, as the sun crosses
the celestial equator going south.
die Zeit der Tagundnachtgeleiche, am Frühlingsanfang der Nordhalbkugel um den 23. September. Die Sonne steht dann im Himmelsäquator und geht für alle Orte der Erde um 6 Uhr Ortszeit im Ostpunkt auf und um 18 Uhr Ortszeit im Westpunkt unter. Zu allen anderen Zeiten sind Tag und Nacht für alle Orte, die nicht auf dem gleichen Breitenkreis liegen, von ungleicher Länge. Die beiden Punkte, an denen sich die Sonne zur Zeit der Tagundnachtgleiche befindet und in denen Ekliptik und Himmelsäquator sich schneiden, heißen Äquinoktialpunkte (Frühlingspunkt oder Widderpunkt und Herbstpunkt oder Waagepunkt). Sie verschieben sich infolge der Präzession. Ihre gedachte Verlängerungslinie wird als Äquinoktiallinie bezeichnet.
culmination:
the passage of a heavenly body across the meridian of a given place. Two
culminations of a body take place in the course of a day, one above and
the other below the celestial pole, called the upper and the lower, respectively.
Durchgang eines Gestirns, auch der Sonne, durch den jeweiligen örtlichen Meridian.
meridian:
imaginary north-south line on the earth's surface that connects both geographic
poles; it is used to indicate longitude.
mittagslinie, Verbindungslinie der Orte, an denen die Sonne gleichzeitig kulminiert, d.h. den höchsten Punkt ihrer scheinbaren Tagesbahn erreicht, oder die zur selben Zeit "Mittag" haben. Kürzeste Verbindung auf der Erdoberfläche von Pol zu Pol.
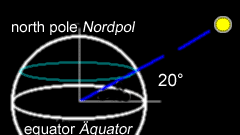
declination:
the solar declination is the latitude of the point on the earth's surface
at which the sun is directly overhead on the day in question.
E.g. on may 21 the sun is directly overhead at 20° north (see image).
|
Date
|
Solar
declination
|
|
Jun
22
(Summer solstice) |
23.4º
N
|
|
May
21
July 24 |
20º
N
|
|
April
16
August 28 |
10º
N
|
|
March
21
September 23 (Equinoxes) |
0º
|
|
February
23 |
10º
S
|
|
January
21
November 22 |
20º
S
|
|
December
22
(Winter solstice) |
23.4º
S
|
Deklination:
die Deklination der Sonne gibt an, über welchem Breitenkreis die
Sonne an diesem Tag genau senkrecht steht.
z.B. am 21. Mai steht sie genau über dem Breitenkreis 20° Nord. (siehe Skizze)
gnomon:
an object that indicates time by position or length of its shadow.
Gnomon:
griech. Schattenzeiger, ein schattenwerfender Stab zur Bestimmung des
Mittags und der Sonnenhöhe.
sunpath, ecliptic:
the great circle that is the apparent sunpath among the constellations
in the course of a year; from another viewpoint the projection on the
celestial sphere of the orbit of the earth around the sun. The constellations
of the zodiac are arranged along the ecliptic. The ecliptic is inclined
about 23.5° to the plane of the celestial equator; the two points
of intersection of the ecliptic and the plane mark the vernal and autumnal
equinoxes.
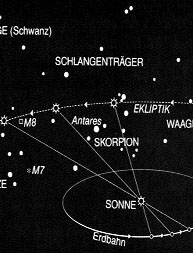
Sonnenbahn
/ Ekliptik:
die scheinbare Bahn der Sonne durch die Tierkreisbilder im Jahreslauf.
Schnitt der Erdbahnebene mit der scheinbaren Himmelskugel.
Durch die Bewegung der Erde scheint die Sonne von Stern zu Stern zu wandern.
lunar orbit:
the moon moves around the earth on an approximately circular orbit, that
is at an angle of 5° 9' to the ecliptic. According to the sidereal
period the moon needs 27d 7h 43min to reach the same position in the
zodiac.
Mondbahn:
der Mond bewegt sich rechtläufig auf einer nahezu kreisförmigen
elliptischen Bahn, deren Ebene um 5° 9' gegen die Ekliptik geneigt
ist, um die Erde. Dabei nimmt er nach der siderische Umlaufzeit von 27d 7h
43min bzgl. der Fixsterne wieder die gleiche Stellung ein. Wegen der gleichzeitigen
Erdbewegung führt der Mond dabei eine Pendelbewegung um die Erdbahn
aus, deren Amplitude etwa nur 1/400 der Entfernung Erde-Sonne beträgt;
durch die Verhältnisse der Bahnradien und der Umlaufzeiten für
die Bewegung des Mondes um die Erde sowie die der Erde um die Sonne bedingt,
ist dabei die Mondbahn immer zur Sonne hin gekrümmt. Heliozentrisch
gesehen bewegt sich der Mond also auf einer durch die Erde stark gestörten
Bahn um die Sonne.
phase of the moon:
The phases of the moon (meaning the different illuminated appearance ot
the moon) depend on the constellation of sun, moon and earth.Within a
month we can observe the different phases of the moon. If the moon is
situated almost between sun and earth, we see its dark side (New Moon).
Full Moon occures when the moon and sun are in opposite positions.
Mondphase:
Die Mondphasen (d.h. die Beleuchtungsformen des Mondes) hängen von
der Konstellation Sonne-Mond-Erde ab. Bei Neumond steht der Mond zwischen
Erde und Sonne, d.h., die der Erde zugewandte Seite ist nicht beleuchtet.
Vollmond tritt ein, wenn der Mond der Sonne gegenüber steht; dann
ist die ganze sichtbare Mondoberfläche beleuchtet. Zwischen Neumond
und Vollmond ist zunehmender Mond, danach abnehmender Mond, mit Halbmond
jeweils in der Mitte.
First
(Last) Quarter:
The appearance of the moon at about a week after New Moon is called First
Quarter. A week after Full Moon is Last Quarter.
Erstes
Viertel (zunehmender Halbmond):
der Mond circa eine Woche nach Neumond
Letztes
Viertel (abnehmender Halbmond)
Der Mond circa eine Woche nach Vollmond
sidereal period:
the time required for a celestrial body within the solar system to complete
one revolution with respect to the fixed stars; i.e., as observed from
some fixed point outside the system. The siderial period of a planet can
be calculated as its synodic period (the time for it to return to the
same position relative to sun and earth) is known; the siderial period
of the moon is the time needed for it to return to the same position against
the background of stars.
die Zeit, die der Planet, von der Sonne aus gesehen, braucht, um 360° in seiner Bahn zurückzulegen.
synodal period:
the time required for a body in the solar system, such as a planet, the
moon, to return to the same or approximately the same position relative
to the sun as seen by an observer on the earth. The moon's synodic period
is the time between successive recurrences of the same phase; e.g., between
Full Moon and Full Moon.
die scheinbare Umlaufzeit, die ein Planet, von der Erde aus gesehen braucht, um in die gleiche Konjunktion zu gelangen. Beim Mond zum Beispiel von Vollmond bis Vollmond.
zodiac:
a belt around the heavens extending 9° on eigther side of the ecliptic,
the plane of the earth's orbit and of the sun's apparent annual path.
The orbits of the moon also lie entirely within the zodiac.
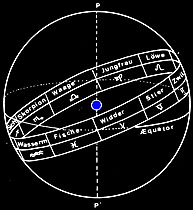
Tierkreis:
auch Zodiak(us) genannt, die Zone beiderseits der Ekliptik, die in 12
Sternbilder, die Tierkreiszeichen eingeteilt ist. Sie wird im Jahr einmal
von der Sonne durchlaufen (von der Erde aus gesehen).
celestial sphere:
the imaginary sphere where - from the observer's point of view -the stars
appear to be projected to. The projection of the earth equator to this
sphere creates the celestial equator. The infinite elongation of
the earth axis builds the celestial axis. Its intersections with
the cel. sphere are called celestial poles (the northern cel. pole is
located close to the Polestar).
Himmelskugel:
gedachte Kugel, an die - vom Betrachter aus gesehen - die Gestirne projiziert
erscheinen. Die Projektion des Erdäquators auf die H. ergibt den
Himmelsäquator, die Verlängerung der Erdachse ins Unendliche
bildet die Himmelsachse, die die H. in den Himmelspolen durchstößt
(der nördl. Himmelspol liegt gegenwärtig in der Nähe des
Polarsterns). Die astronomischen Orte der Gestirne an der H. werden
durch die astronomischen Koordinaten festgelegt.